Need support?
Call us and get support from one of our advisors.
Call for Free 877-403-8834

Auricular hematoma, also known as cauliflower ear, is a condition caused by an injury to the outer ear. Learn more about how it happens and why preventing it is important.
What is auricular hematoma? The definition of this medical term is a buildup of blood underneath the skin of the outer ear. It is also sometimes called a “pinna hematoma” because it develops on the pinna (the outer part of the ear), but you might know it by its more common name, “cauliflower ear.”
Individual auricular hematoma causes vary, but ultimately, it’s due to an injury that tears apart layers of ear tissue or damages the cartilage (the stiff material that gives your ears their shape). Blood then collects where the injury occurred. If left untreated, scarring causes the puffy and puckered look that led to the name “cauliflower ear.” Injuries that lead to auricular hematoma are associated with:
But, besides trauma, what could cause auricular hematoma? There are a few possibilities:
If you’ve had an ear injury, pay attention to auricular hematoma symptoms such as:
As doctors work to identify your condition, they have to consider other causes that may have similar looks or characteristics, in order to rule them out. This is called “differential diagnosis”.2 For auricular hematoma, differential diagnosis conditions might include:
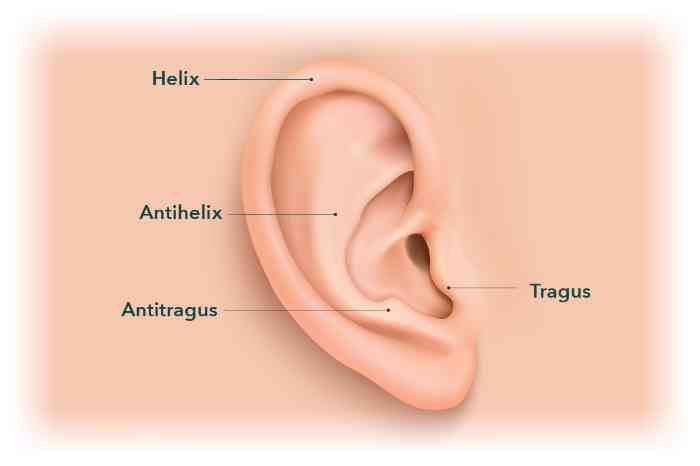
Each section of the ear has a specialized medical name, so let’s look at the spots where auricular hematomas form most often:
However, hematomas can form in other places around and in the ear as well.
There are a few kinds of auricular hematoma treatments, but it’s always advised that if you have an ear injury, you should see a doctor as soon as you can.
Auricular hematomas have a high tendency to reoccur — and the hole-punch technique was developed to prevent that from happening.
In this procedure, doctors make an incision in the ear and then use a tool to punch tiny holes in the cartilage. These holes allow the tissue layers under the cartilage and on top of the cartilage to come into contact. When they heal together, it tightens the tissue and there is less room for a hematoma to reform.
Post-auricular hematoma treatment is important and needs to be monitored carefully to prevent the tissue from separating again and allowing another clot to form. The key to this is constant pressure on the ear, which can be done in a few ways. Before attempting the treatment options below, consult with your doctor to ensure it is safe and appropriate for your condition.
Auricular hematoma complications can be simply cosmetic — or more serious.
1 Halil E. Özel, Selahattin Genç, Erkan Esen, Fatih Özdoğan, Adin Selçuk, Auricular hematoma cases caused by mobile phones, Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Cases, Volume 1, Issue 4, 2015, ISSN 2214-5419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omsc.2015.10.002.
2 Hohman MH, Jamal Z, Krogmann RJ, et al. Auricular Hematoma. [Updated 2024 May 1]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK531499/.
3 Putri IL, Bogari M, Khoirunnisa A, Dhafin FR, Kuswanto D. Surgery of Severe Cauliflower Ear Deformity. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2023 Apr 19;11(4):e4953. doi: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000004953. PMID: 37091928; PMCID: PMC10115543. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10115543/.