Need support?
Call us and get support from one of our advisors.
Call for Free 877-403-8834

Struggling with ear pressure, discomfort, or hearing issues? Eustachian tube dysfunction could be the culprit. In this article, we’ll explore its causes, symptoms, and effective treatments to help you regain comfort and improve your ear health.
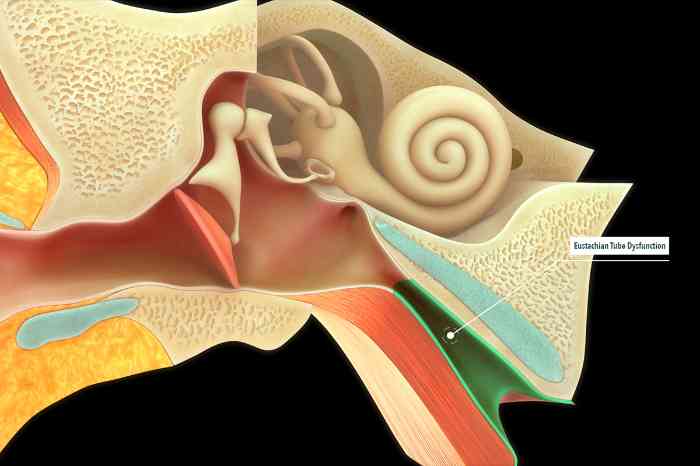
When our Eustachian tubes function properly, we don’t think about them. However, Eustachian tube dysfunction can cause pain and discomfort.
Eustachian tube dysfunction occurs when the Eustachian tubes, which connect your middle ear to your throat to ventilate the eardrum, become clogged.
This can lead to a feeling of pressure or fullness in the ear, muffled hearing and even ear pain. Eustachian tube dysfunction often occurs as a result of colds or allergies.
There are four main types of Eustachian tube dysfunction (ETD):
● Patulous Eustachian tube dysfunction
● Obstructive Eustachian tube dysfunction
● Baro-challenge-induced Eustachian tube dysfunction
● Chronic Eustachian tube dysfunction
Learn more about each of these types of Eustachian tube dysfunctions below.
Eustachian tube dysfunction symptoms vary depending upon the cause. However, these symptoms are most common:
Patients with Patulous Eustachian tube dysfunction seldom experience pain. Instead, they may hear their own voice, heartbeat or breathing loudly. This rare condition, called autophony, is caused by the open Eustachian tube allowing these sounds to more easily reach the middle ear.²
Obstructive Eustachian tube dysfunction causes more pain and pressure because the tube is blocked, and fluid builds up in the middle ear. Muffled hearing and popping and crackling sounds are also symptoms of this type of Eustachian tube dysfunction. Dizziness can also occur.
Patients with baro-challenge-induced Eustachian tube dysfunction may experience pain and pressure during altitude changes, particularly when flying or driving.
The most common Eustachian tube dysfunction stems from a colds, allergies or other respiratory illnesses. When the Eustachian tubes become inflamed, mucus builds up, resulting in Eustachian tube dysfunction. It can also result from the swollen adenoids, as well as exposure to pollutants or smoke.³
Diagnosis of Eustachian tube dysfunction can be difficult because there is no specific test for the condition, which can mimic tinnitus and earaches.⁴
A doctor may use several tests when diagnosing Eustachian tube dysfunction. Usually a doctor examines the eardrum and may ask you to swallow or breathe deeply to see how the eardrum responds. This is often followed with a tympanometry test, which reveals how your middle ear is functioning.
Hearing tests may also be used to determine whether there is hearing loss.
Tympanometry tests are the most common way to diagnose Eustachian tube dysfunction.
A small probe, which resembles an earphone, is placed in the ear. The probe varies the air pressure in the ear canal, moving from positive to negative pressure.⁵ The tympanometer then displays a graph, the tympanogram, that shows how well your eardrum moves.
The different shapes of tympanograms indicate various middle ear conditions. Shapes may suggest fluid behind the eardrum (common in otitis media) or a perforation. The shape may also indicate eustachian tube dysfunction or early stages of fluid buildup.
Wondering how to fix Eustachian tube dysfunction? Treatment for dysfunctional Eustachian tubes ranges from home remedies to medical treatment options. Learn more about treatment options below.
Eustachian tube dysfunction symptoms are usually mild and often resolve on their own. However, there are Eustachian tube dysfunction remedies you can try at home, including taking certain vitamins and various exercises and jaw movements.
Vitamins for Eustachian tube dysfunction and overall hearing health include those with antioxidant properties⁶:
Consult with your doctor before adding any vitamins or supplements to ensure it is right for you.
Eustachian tube dysfunction exercises include⁷:
In cases where chronic Eustachian tube dysfunction occurs, medical treatments may be required. Medical treatments for Eustachian tube dysfunction can include:
● Surgery for Eustachian tube dysfunction
● Acupuncture for Eustachian tube dysfunction
Eustachian tube dysfunction surgery methods include⁸:
If Eustachian tube dysfunction stems from a cold or allergies, it usually clears up in a few days to a week. In cases of chronic Eustachian tube dysfunction, symptoms last more than three months.⁹
Pressure changes that occur during airplane flights can cause pain and discomfort for those flying with Eustachian tube dysfunction. Yawning, swallowing and chewing gum during takeoff and landing may help alleviate these challenges for those with Eustachian tube dysfunction. The Valsalva Maneuver may also help. The Valsalva Maneuver involves pinching your nostrils and keeping your mouth closed while gently blowing, as if you are blowing your nose.
Yes, Eustachian tube dysfunction can be cured. Start with a visit to your ear, nose and throat specialist to identify and eliminate the cause.
Depending on the cause and whether the condition is chronic, the doctor may recommend medications or a surgical approach, such as pressure equalization tubes or balloon Eustachian tube dilation.¹¹
2 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7346684/.
3 https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamaotolaryngology/fullarticle/2825855.
7 https://www.amplifonusa.com/hearing-loss/blog/managing-eustachian-tube-dysfunction.
8 https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamaotolaryngology/fullarticle/2825855.
9 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK555908/.
10 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK262265/.
11 https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamaotolaryngology/fullarticle/2825855.